The initial assessment and examination play a crucial role in the management of trauma patients. Upon arrival, the healthcare team must quickly assess the patient's vital signs, airway patency, breathing effort, and circulation status. This includes checking for any obvious external bleeding or signs of shock such as pallor or altered mental status. Additionally, it is important to obtain a detailed history from both the patient and any available witnesses to gather information about the mechanism of injury and associated symptoms.
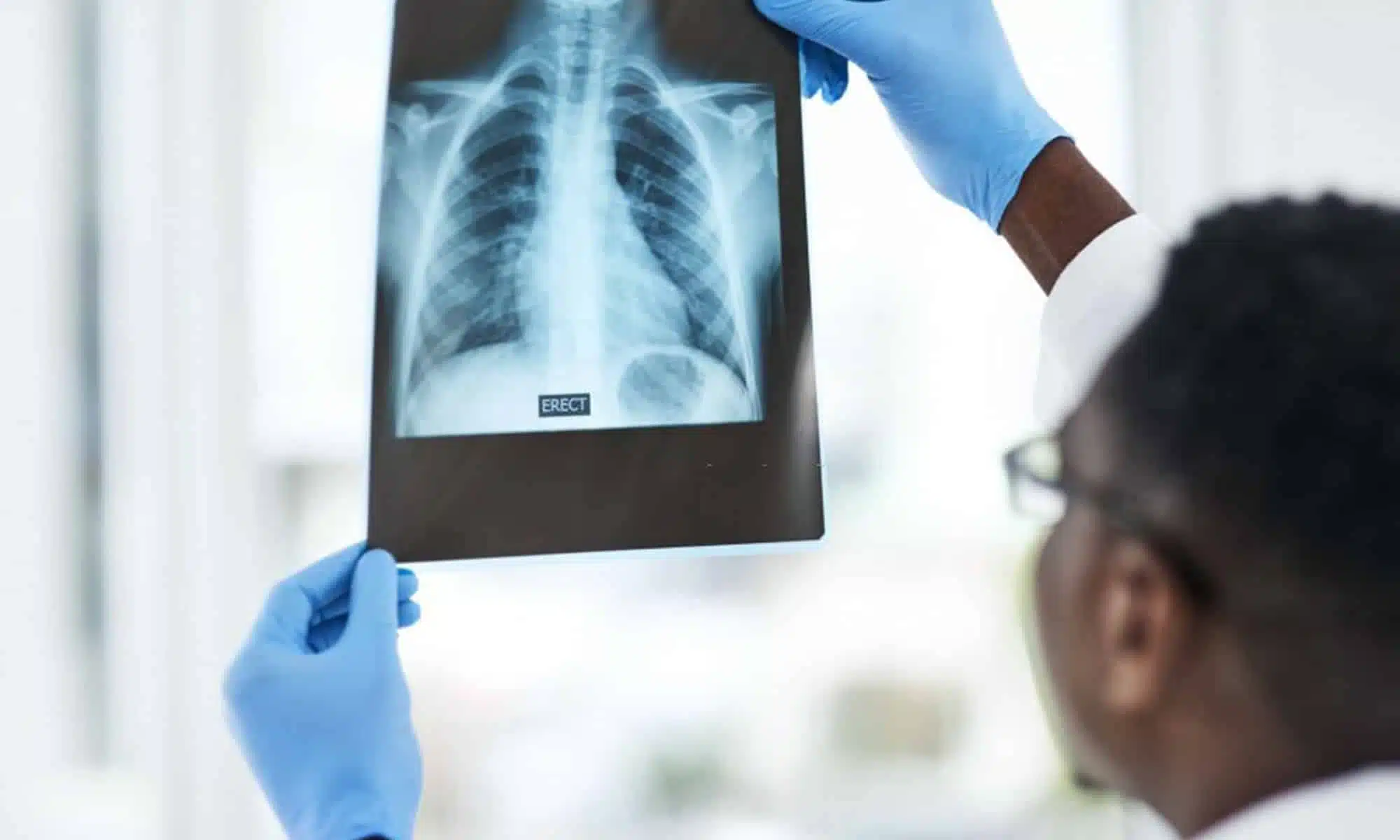
Diagnostic procedures are then initiated to further evaluate the extent of injuries sustained by the trauma patient. These may include imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds to identify fractures, internal organ damage, or other abnormalities. Laboratory tests are also conducted to assess blood counts, coagulation profiles, and markers of organ dysfunction. These diagnostic tools aid in determining appropriate treatment plans tailored specifically for each individual case.
Stabilization and breathing support are paramount during this early phase of trauma management. The healthcare team ensures that the patient's airway is secured through techniques like intubation if necessary while simultaneously providing adequate oxygenation and ventilation support using mechanical ventilators if indicated. In cases where rib fractures are present causing compromised respiratory function due to pain or flail chest deformities leading to paradoxical movement of chest wall segments with respiration assistance with analgesics along with close monitoring becomes essential.
Diagnostic procedures play a crucial role in determining the extent of injuries sustained during traumatic events. One important procedure is imaging, such as X-rays and CT scans, which can provide detailed images of bones, organs, and soft tissues. These imaging techniques help identify fractures, internal bleeding, or other abnormalities that may not be immediately visible.
In addition to imaging, laboratory tests are often conducted to assess various aspects of a patient's health. Blood tests can indicate the presence of infection or abnormal blood clotting. Urine tests may reveal kidney damage or urinary tract infections. Furthermore, electrocardiograms (ECGs) are useful for evaluating cardiac function and detecting any potential heart abnormalities.
Furthermore, physical examinations by healthcare professionals are an essential component of diagnostic procedures. They involve assessing vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation levels to determine the overall condition of the patient. Additionally, palpation and auscultation techniques allow healthcare providers to evaluate specific areas for tenderness or abnormal sounds that could indicate internal injuries.
By utilizing a combination of imaging techniques like X-rays and CT scans along with laboratory tests and physical examinations performed by skilled healthcare professionals; accurate diagnosis becomes possible in trauma cases. This comprehensive approach enables medical teams to quickly identify injuries so that appropriate treatment plans can be developed promptly without delay.
Stabilization and Breathing Support are crucial aspects of managing patients with chest trauma. The primary goal is to ensure adequate oxygenation and ventilation while addressing any life-threatening injuries. Immediate attention should be given to securing the airway, providing supplemental oxygen, and monitoring respiratory status.
In cases of severe chest trauma, endotracheal intubation may be necessary to maintain a patent airway. This procedure involves inserting a tube through the mouth or nose into the trachea to facilitate mechanical ventilation. It allows for better control over breathing parameters and protects against aspiration of blood or other debris.
Simultaneously, efforts must be made to stabilize breathing by addressing any underlying lung injuries. Chest tubes may need to be inserted if there is evidence of pneumothorax or hemothorax, which can cause lung collapse or compromise gas exchange. These tubes help drain accumulated air or fluid from the pleural space, restoring normal lung function.
Additionally, pain management plays an essential role in stabilizing breathing in patients with rib fractures or flail chest. Adequate analgesia not only improves patient comfort but also encourages deep breathing and prevents complications such as atelectasis or pneumonia due to shallow respirations.
By promptly initiating stabilization measures and providing appropriate respiratory support, healthcare professionals can significantly improve outcomes for patients with chest trauma. Early intervention ensures optimal oxygenation and ventilation while minimizing further damage caused by inadequate respiration.
Rib fractures are a common injury that can occur due to trauma or other underlying medical conditions. The management of rib fractures aims to alleviate pain, promote healing, and prevent complications such as pneumonia or respiratory distress.
Initial treatment for rib fractures involves providing adequate pain relief through the use of analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). This helps improve patient comfort and facilitates deep breathing and coughing exercises, which are essential for preventing lung infections. In some cases, localized anesthesia techniques may be employed to provide targeted pain relief.
In addition to pain management, the use of chest binders or supportive devices can help stabilize the fractured ribs and reduce discomfort during movement. These devices wrap around the chest wall tightly but should not impede normal breathing patterns. They provide external support to the injured area, allowing for better alignment of the fractured bones and reducing strain on surrounding muscles.
Furthermore, physical therapy plays a crucial role in rib fracture management. Early mobilization with gentle range-of-motion exercises helps maintain flexibility in surrounding muscles while preventing stiffness or atrophy. Gradually increasing activity levels under professional guidance aids in restoring strength and function without causing further damage. It is important for patients with rib fractures to follow their healthcare provider's recommendations regarding exercise intensity and frequency to ensure optimal recovery.
By implementing these measures promptly after diagnosis, healthcare professionals can effectively manage rib fractures by addressing pain relief, stabilization through supportive devices, as well as promoting proper healing through physical therapy interventions. Such comprehensive care reduces complications associated with this injury while facilitating a quicker return to normal daily activities for patients.
Pneumothorax and hemothorax are serious medical conditions that require prompt treatment to prevent further complications. The primary goal of treatment is to restore normal lung function and alleviate symptoms.
Initially, a chest X-ray or CT scan may be performed to confirm the presence of pneumothorax or hemothorax. If the condition is severe or causing respiratory distress, immediate intervention may be necessary. In cases of tension pneumothorax, a needle decompression procedure may be performed to release trapped air from the pleural space and relieve pressure on the lungs.
Once diagnosed, treatment options for pneumothorax and hemothorax include drainage procedures such as thoracentesis or tube thoracostomy. These procedures involve inserting a small tube into the chest cavity to remove excess air or blood accumulation. In some cases, surgery may be required to repair any underlying damage and prevent recurrence.
The follow-up care for patients with pneumothorax and hemothorax involves monitoring lung function through regular imaging studies and clinical examinations. It is important for individuals who have experienced these conditions to avoid activities that could put excessive strain on their lungs, such as heavy lifting or smoking. Additionally, counseling and psychological support should be provided as these conditions can have significant emotional impact on patients' well-being.
Flail chest, a serious injury resulting from multiple rib fractures, requires prompt and appropriate management. The primary goal in treating flail chest is to stabilize the affected area and restore normal breathing patterns. This can be achieved through various techniques such as pain management, respiratory support, and surgical interventions if necessary.
One of the key aspects in managing flail chest is providing adequate pain control to alleviate discomfort and facilitate effective breathing. Analgesic medications are commonly administered to reduce pain levels, allowing patients to breathe more comfortably. Additionally, non-pharmacological methods like positioning techniques may be employed to minimize pain associated with movement or coughing.
Respiratory support plays a crucial role in optimizing lung function for individuals with flail chest. Techniques such as oxygen therapy and non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) are often utilized to improve oxygenation and maintain proper ventilation. These interventions help prevent complications like atelectasis or pneumonia that may arise due to inadequate lung expansion.
In summary, successful management of flail chest involves addressing both the physical trauma caused by rib fractures as well as ensuring proper respiratory support for optimal lung function. Prompt administration of analgesics for pain relief along with respiratory interventions like oxygen therapy or NIPPV can significantly improve patient outcomes. By implementing these strategies effectively, healthcare professionals aim to stabilize the injured area while promoting efficient breathing patterns during the recovery process.
Cardiac injuries can occur as a result of trauma, and prompt assessment is crucial to ensure timely intervention. When evaluating a patient with suspected cardiac injury, it is important to consider the mechanism of injury, such as blunt or penetrating trauma. Additionally, assessing vital signs including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation can provide valuable information about the severity of the injury.
One key aspect of cardiac injury assessment involves conducting a thorough physical examination. This includes auscultation for abnormal heart sounds or murmurs that may indicate damage to the myocardium or valves. Palpating for chest wall tenderness or crepitus can help identify potential rib fractures that could be associated with underlying cardiac injury. Moreover, examining peripheral pulses and skin color can offer insights into possible compromise in circulation.
Diagnostic tests play a critical role in confirming cardiac injuries and guiding further management. Electrocardiography (ECG) should be performed early on to assess for any arrhythmias or ischemic changes indicative of myocardial damage. Cardiac enzymes like troponin levels are essential markers for detecting myocardial cell death following an acute insult. Imaging studies such as echocardiography or computed tomography (CT) scans may also be employed to visualize structural abnormalities within the heart chambers or detect pericardial effusion.
By carefully considering the mechanism of injury alongside comprehensive physical examination findings and appropriate diagnostic tests, healthcare providers can effectively evaluate patients with suspected cardiac injuries. Early identification allows for timely interventions aimed at minimizing complications associated with these potentially life-threatening conditions.
Treatment of Cardiac Contusions requires a comprehensive approach to manage the potential complications and ensure optimal patient outcomes. The primary goal is to stabilize the patient's condition and relieve symptoms while promoting healing and preventing further damage.
Initially, patients with suspected cardiac contusions should be closely monitored in a critical care setting. This involves continuous monitoring of vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation levels. In severe cases, immediate intervention may be necessary to restore normal heart function through methods such as defibrillation or cardioversion.
Diagnostic procedures play a crucial role in determining the extent of cardiac injury and guiding treatment decisions. These may include electrocardiography (ECG), echocardiography, cardiac enzyme tests, chest X-rays, or coronary angiography. These tests help identify any abnormalities in heart rhythm or structure that may require specific interventions.
Once stabilized, management focuses on pain control and supportive measures for optimal recovery. Pain medications are administered as needed to alleviate discomfort associated with contusion-related symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath. Additionally, bed rest is typically recommended initially to minimize physical exertion on the injured heart muscle.
To summarize these points,
• Treatment of Cardiac Contusions requires a comprehensive approach to manage potential complications and ensure optimal patient outcomes.
• The primary goal is to stabilize the patient's condition, relieve symptoms, promote healing, and prevent further damage.
• Patients with suspected cardiac contusions should be closely monitored in a critical care setting.
• Continuous monitoring of vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation levels is essential.
• In severe cases, immediate intervention may be necessary to restore normal heart function through methods like defibrillation or cardioversion.
• Diagnostic procedures like electrocardiography (ECG), echocardiography, cardiac enzyme tests, chest X-rays, or coronary angiography play a crucial role in determining the extent of cardiac injury and guiding treatment decisions.
• These tests help identify any abnormalities in heart rhythm or structure that may require specific interventions.
• Once stabilized, management focuses on pain control and supportive measures for optimal recovery.
• Pain medications are administered as needed to alleviate discomfort associated with contusion-related symptoms such as chest pain or shortness of breath.
• Bed rest is typically recommended initially to minimize physical exertion on the injured heart muscle.
Internal organ injury evaluation is a critical step in assessing and managing trauma patients. The primary goal of this evaluation is to identify any potential damage or dysfunction to the internal organs, such as the liver, spleen, kidneys, or intestines. This process involves a thorough physical examination, including palpation and percussion techniques, to assess for tenderness or abnormal masses.
In addition to the physical examination, diagnostic imaging plays a vital role in evaluating internal organ injuries. Imaging modalities like CT scans or ultrasound can provide detailed images of the affected organs and help determine the extent of injury. These tests allow healthcare professionals to identify specific injuries such as lacerations, contusions, or hematomas.
Once internal organ injuries are identified through evaluation and diagnostic procedures, appropriate management strategies can be implemented promptly. Treatment options may include surgical interventions for severe cases requiring immediate intervention or conservative measures for less severe injuries that can be managed with close monitoring and supportive care.
The evaluation of internal organ injuries requires meticulous attention to detail and expertise from healthcare providers. By identifying these injuries accurately and promptly initiating appropriate treatment plans based on their severity, patient outcomes can be optimized while minimizing complications associated with delayed diagnosis or inadequate management strategies.
Counseling and psychological support play a crucial role in the overall management of patients who have experienced traumatic injuries. Following initial assessment and examination, it is important to address the emotional well-being of these individuals. Trauma can often lead to feelings of anxiety, fear, and depression, which may hinder their recovery process. By providing counseling services, healthcare professionals aim to support patients in coping with their emotions and promoting mental resilience.
One aspect of counseling involves helping patients develop effective coping mechanisms for managing stress and anxiety related to their injury. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises or mindfulness practices can be taught to help individuals regain a sense of control over their emotions. Additionally, counselors may explore any underlying issues that could potentially affect the patient's ability to adapt during the recovery period.
Psychological support also extends beyond individual therapy sessions. Support groups are an invaluable resource for trauma survivors as they provide a platform for sharing experiences and fostering connections with others who have gone through similar challenges. These groups offer a safe space where individuals can express themselves without judgment while receiving encouragement from peers who understand firsthand what they are going through.
By integrating counseling and psychological support into the comprehensive care plan for trauma patients, healthcare providers acknowledge the importance of addressing not only physical injuries but also emotional well-being. This holistic approach promotes healing on multiple levels and contributes significantly to long-term recovery outcomes.
Counseling and psychological support are aimed at addressing the emotional and psychological well-being of individuals who have experienced trauma or injury, providing them with the necessary support and guidance to cope with their situation.
An initial assessment and examination are conducted upon arrival of a patient to evaluate their condition and identify any immediate medical needs.
Diagnostic procedures are employed to identify and determine the extent of injuries or trauma, helping healthcare professionals develop appropriate treatment plans.
Stabilization and breathing support are vital aspects of medical care aimed at ensuring the patient's vital signs are stable and that they can breathe properly.
Rib fracture management typically involves pain control, respiratory support, and close monitoring to prevent potential complications such as pneumonia.
Treatment for pneumothorax and hemothorax involves the evacuation of air or blood from the chest cavity, typically through the use of a chest tube or needle aspiration.
Flail chest management may include pain control, respiratory support, and in severe cases, surgery to stabilize the affected area.
The assessment of cardiac injury involves a thorough evaluation of the heart's function and any potential damage it may have sustained.
Treatment for cardiac contusions may involve medication to manage symptoms and support cardiac function, as well as close monitoring to ensure the injury heals properly.
The evaluation of internal organ injury typically involves imaging techniques such as CT scans or ultrasounds to identify any damage and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Counseling and psychological support provide individuals with a safe space to express their emotions, cope with trauma, and develop strategies to navigate their recovery process.
Copyright © Car Accident Doctors Group. All Rights Reserved