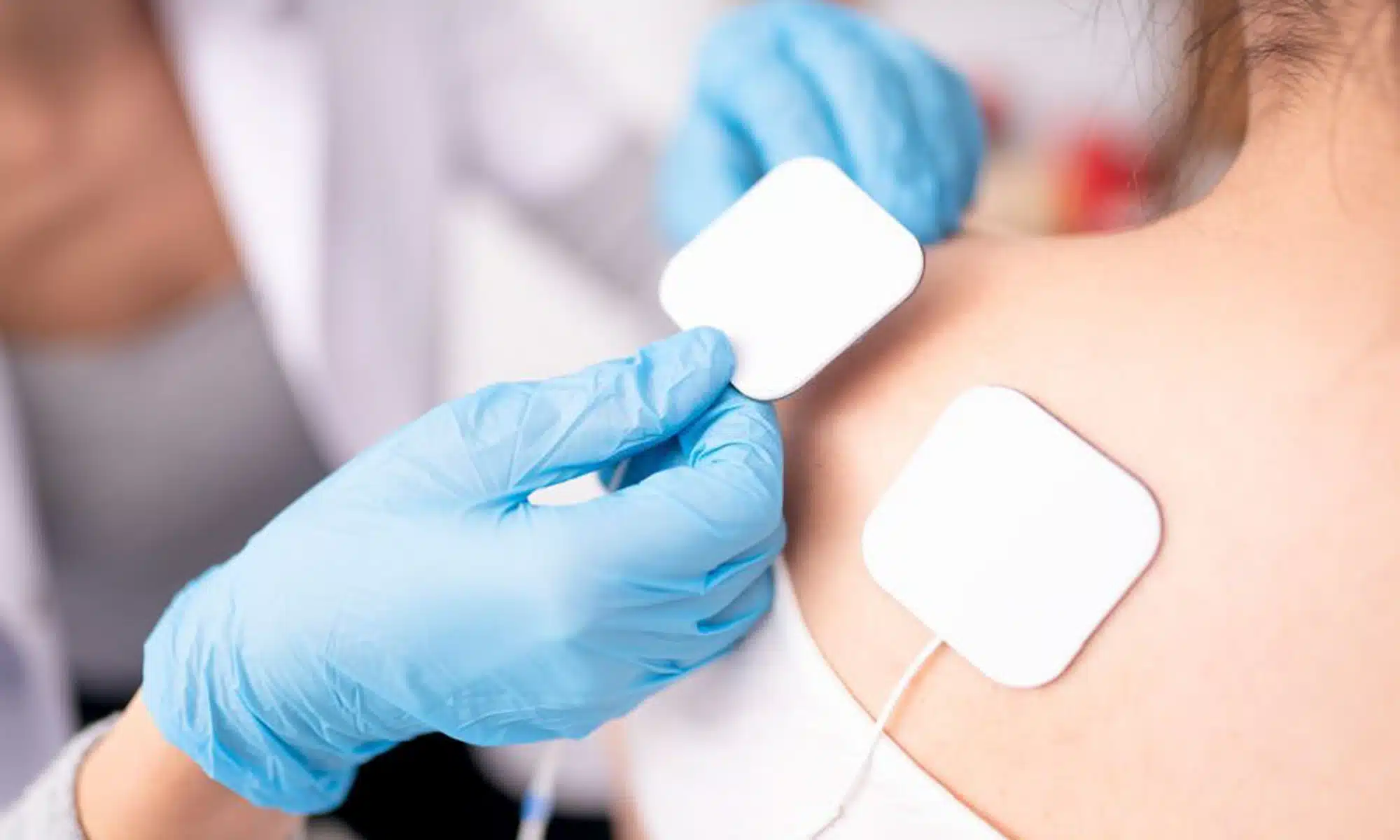
Electrical stimulation is a therapeutic technique that involves the use of electrical currents to stimulate nerves and muscles in order to promote healing and relieve pain. This non-invasive treatment method has been widely used in various medical fields, including physical therapy, sports medicine, and rehabilitation.
One of the key aspects of pre-treatment evaluation for electrical stimulation is assessing the patient's condition and determining whether they are suitable candidates for this type of therapy. Factors such as the nature and severity of their injury or condition, their overall health status, and any potential contraindications need to be carefully considered before proceeding with electrical stimulation.
There are different types of electrical stimulation techniques available depending on the specific needs of each patient. These include transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), which uses low-frequency currents to target pain receptors; neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES), which focuses on stimulating muscle contractions; and functional electrical stimulation (FES), which aims to restore function by activating specific muscles or muscle groups. Each type has its own unique benefits and applications within the realm of electrical stimulation therapy.
By understanding these fundamental concepts surrounding electrical stimulation, healthcare professionals can effectively incorporate this technique into their treatment plans. With proper evaluation, selection of appropriate techniques, integration with other therapies when necessary, along with adequate patient education about expected outcomes and precautions involved in this form of treatment, individuals can experience improved healing processes while managing pain effectively.
The pre-treatment evaluation is a crucial step in determining the suitability of electrical stimulation therapy for an individual. It involves a comprehensive assessment of the patient's medical history, current condition, and specific goals for treatment. The evaluation begins with a detailed interview to gather information about any previous injuries or surgeries, underlying health conditions, and medications being taken.
Next, a physical examination is conducted to assess the patient's range of motion, muscle strength, and overall mobility. This helps identify any areas of weakness or dysfunction that may benefit from electrical stimulation therapy. Additionally, diagnostic tests such as X-rays or MRI scans may be ordered to further evaluate the extent of injury or damage.
In some cases, it may be necessary to consult with other healthcare professionals involved in the patient's care to ensure a holistic approach. This could include collaborating with orthopedic surgeons, neurologists, or physical therapists who can provide valuable insights into the patient's condition and help determine if electrical stimulation therapy is appropriate.
Overall, the pre-treatment evaluation plays a vital role in guiding clinicians towards developing an effective treatment plan tailored specifically to each individual patient's needs. By thoroughly assessing their medical history and conducting comprehensive examinations, healthcare providers can make informed decisions regarding whether electrical stimulation therapy is suitable and how it should be implemented for optimal outcomes.
Electrical stimulation is a widely used therapeutic technique that involves the application of electrical currents to specific areas of the body. It can be used for various indications, including pain management, muscle strengthening and re-education, tissue healing, and nerve stimulation. One common indication for electrical stimulation is in the treatment of chronic pain conditions such as low back pain, neck pain, and fibromyalgia. By targeting the nerves responsible for transmitting pain signals to the brain, electrical stimulation can help reduce or eliminate pain sensations.
Another indication for electrical stimulation is in muscle rehabilitation and re-education. This technique can be particularly beneficial for individuals who have experienced muscle weakness or loss of function due to injury or neurological conditions such as stroke or spinal cord injury. Electrical currents are applied directly to the muscles through electrodes placed on the skin surface, causing them to contract and relax in a controlled manner. This helps improve muscle strength, coordination, and range of motion.
Additionally, electrical stimulation has been found effective in promoting tissue healing by increasing blood flow and oxygenation to injured areas. It can be used in cases of wound healing difficulties or musculoskeletal injuries such as fractures or tendonitis. The application of electrical currents stimulates cellular activity within tissues, enhancing their ability to repair themselves.
In summary, electrical stimulation offers several indications ranging from pain management to muscle rehabilitation and tissue healing promotion. By targeting specific nerves responsible for transmitting pain signals, It effectively reduces discomfort associated with chronic conditions. Moreover, this therapy aids in restoring weakened muscles by contracting them through controlled electric impulses. It also promotes tissue healing by stimulating cellular activity within injured areas. Overall, electrical stimulation provides a versatile approach towards improving patient outcomes across different medical fields
• Electrical stimulation can be used for pain management, muscle strengthening and re-education, tissue healing, and nerve stimulation.
• It is commonly used in the treatment of chronic pain conditions such as low back pain, neck pain, and fibromyalgia.
• By targeting the nerves responsible for transmitting pain signals to the brain, electrical stimulation can help reduce or eliminate pain sensations.
• Electrical stimulation is beneficial for individuals who have experienced muscle weakness or loss of function due to injury or neurological conditions such as stroke or spinal cord injury.
• It improves muscle strength, coordination, and range of motion by causing muscles to contract and relax in a controlled manner.
• Electrical stimulation promotes tissue healing by increasing blood flow and oxygenation to injured areas.
• It can be used in cases of wound healing difficulties or musculoskeletal injuries such as fractures or tendonitis.
• The application of electrical currents stimulates cellular activity within tissues, enhancing their ability to repair themselves.
Electrical stimulation is a therapeutic technique that involves the application of electrical currents to specific areas of the body. This technique can be used to treat various conditions and promote healing. There are several types of electrical stimulation, each with its own unique benefits and applications.
One common type of electrical stimulation is transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS). TENS uses low-frequency electrical currents to stimulate sensory nerves and provide pain relief. It can be particularly effective in treating chronic pain conditions such as arthritis or fibromyalgia. TENS units are portable devices that can be easily used at home, allowing patients to manage their pain on their own.
Another type of electrical stimulation is neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES). NMES targets motor nerves and muscles, helping to improve muscle strength and function. This type of stimulation is often used in rehabilitation settings for patients recovering from injuries or surgeries. By stimulating the muscles directly, NMES can help prevent muscle wasting and improve overall mobility.
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) is another important type of electrical simulation that aims to restore lost or impaired bodily functions. FES uses small pulses of electricity to activate paralyzed muscles, allowing individuals with spinal cord injuries or neurological disorders to regain movement in affected limbs. This technique has shown promising results in improving quality of life for those with limited mobility.
Electrical stimulation is a therapeutic technique that involves the use of electrical currents to stimulate nerves and muscles in order to alleviate pain, improve muscle strength, and promote tissue healing. The treatment process typically begins with an initial assessment by a healthcare professional who will evaluate the patient's condition and determine if electrical stimulation is appropriate.
Once it has been determined that electrical stimulation is suitable for the patient, the next step in the treatment process involves selecting the appropriate type of electrical stimulation. There are various types available, including transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES), and functional electrical stimulation (FES). Each type targets different areas or functions within the body and may be used alone or in combination with other therapies.
After selecting the appropriate type of electrical stimulation, electrodes are placed on specific areas of the body as directed by a healthcare professional. These electrodes deliver controlled doses of electric current to targeted nerves or muscles. The intensity level can be adjusted based on individual tolerance and response. Treatment sessions typically last for a specified duration, which may vary depending on factors such as severity of symptoms and desired outcomes.
It is important for patients undergoing electrical stimulation therapy to follow their prescribed treatment plan consistently to achieve optimal results. Regular communication with healthcare professionals throughout the treatment process allows adjustments to be made as needed. By adhering to these guidelines, patients can maximize their benefits from this effective modality without experiencing any adverse effects.
Electrical stimulation therapy offers a wide range of benefits for patients undergoing rehabilitation or seeking pain relief. One significant advantage is its ability to promote muscle strengthening and re-education. By delivering electrical impulses directly to the targeted muscles, this therapy helps to stimulate muscle contractions and improve overall strength. Moreover, it can aid in restoring normal movement patterns by activating weakened or paralyzed muscles.
Another key benefit of electrical stimulation is pain management. This therapy has been found effective in reducing both acute and chronic pain levels. By stimulating sensory nerves, electrical impulses can help block pain signals from reaching the brain, providing temporary relief for various conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and nerve injuries.
In addition to muscle strengthening and pain reduction, electrical stimulation also plays a crucial role in promoting tissue healing and injury recovery. The application of specific waveforms during treatment sessions can enhance blood circulation to injured areas, accelerate tissue repair processes, reduce inflammation, and facilitate faster healing times. As a result, patients may experience improved recovery outcomes following surgeries or traumatic injuries without relying solely on medication-based approaches.
By harnessing the power of electrical impulses within controlled therapeutic settings, individuals can reap numerous benefits from electrical stimulation therapy including enhanced muscle function and strength development, reduced pain levels across different conditions,and accelerated tissue healing processes after injuries or surgeries.
It is important to consider certain precautions when using electrical stimulation as a treatment modality. Firstly, individuals with pacemakers or other implanted electronic devices should avoid electrical stimulation due to the potential interference it may cause. Additionally, caution must be exercised in patients with epilepsy or seizure disorders, as electrical stimulation could potentially trigger seizures. Furthermore, individuals who have open wounds or skin infections at the site of application should refrain from undergoing electrical stimulation until the area has fully healed.
Another precautionary measure involves adjusting the intensity of electrical stimulation according to individual tolerance levels. It is crucial to start with low intensities and gradually increase them based on patient response and comfort level. This ensures that adverse effects such as discomfort, pain, or muscle spasms are minimized during treatment sessions.
In terms of contraindications for electrical stimulation, pregnant women should avoid this therapy unless specifically recommended by their healthcare provider. The safety of electrical stimulation during pregnancy has not been extensively studied; therefore, it is best to err on the side of caution. Moreover, individuals with cancerous tumors in close proximity to the treatment area should not undergo electrically stimulated therapies without consulting an oncologist first.
By understanding these precautions and contraindications associated with electrical stimulation therapy, healthcare professionals can ensure safe and effective implementation while minimizing any potential risks for their patients.
Integration with Other Therapies plays a crucial role in maximizing the benefits of electrical stimulation. By combining electrical stimulation with other treatment modalities, healthcare professionals can create a comprehensive and tailored approach to address various conditions and symptoms.
One common integration is the combination of electrical stimulation with physical therapy. Physical therapists often use electrical stimulation alongside exercises to enhance muscle strength, improve range of motion, and promote tissue healing. The targeted application of electrical currents can help facilitate muscle contractions during specific movements or exercises, leading to improved outcomes for patients recovering from injuries or surgeries.
Another effective integration is the combination of electrical stimulation with pain management techniques. For individuals experiencing chronic pain, such as those with neuropathy or fibromyalgia, integrating electrical stimulation with medications or alternative therapies like acupuncture can provide significant relief. Electrical stimulation helps modulate pain signals by stimulating nerves and promoting the release of endorphins, thereby reducing discomfort and improving overall quality of life.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring how electrical stimulation can be integrated into cognitive rehabilitation programs for individuals with neurological disorders such as stroke or traumatic brain injury (TBI). By targeting specific areas of the brain through transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), researchers aim to enhance neuroplasticity and promote functional recovery. Integrating tDCS with other cognitive therapies may lead to improved cognitive function and better long-term outcomes for these patients.
The integration of electrical stimulation with other therapies allows healthcare professionals to take advantage of synergistic effects that can optimize treatment outcomes. Whether it's combining it with physical therapy for musculoskeletal conditions, pain management techniques for chronic discomfort, or cognitive rehabilitation programs for neurological disorders – integrating electrical stimulation expands treatment options and enhances patient care.
Electrical stimulation therapy has been proven to be highly effective in various medical conditions, with several expected outcomes. One of the primary goals of electrical stimulation is pain relief. By stimulating the nerves and muscles, this therapy can help reduce pain intensity and frequency in individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia or neuropathy.
Another expected outcome of electrical stimulation is improved muscle strength and function. This therapy can activate weakened muscles, helping them regain strength and mobility. For patients recovering from injuries or surgeries that have caused muscle weakness or atrophy, electrical stimulation can play a crucial role in enhancing their rehabilitation process.
Furthermore, electrical stimulation has shown promising results in promoting tissue healing and reducing inflammation. By increasing blood flow to the affected area and facilitating nutrient delivery, this therapy accelerates the body's natural healing processes. Additionally, it helps decrease swelling and edema by improving lymphatic drainage.
Overall, electrical stimulation offers a range of positive outcomes for patients seeking pain relief, enhanced muscle function, and accelerated healing. With its ability to target specific areas of concern through different types of electrical currents, this therapeutic approach holds great potential for improving quality of life for individuals dealing with various medical conditions.
Patient Education plays a crucial role in ensuring the success of electrical stimulation therapy. Patients should be well-informed about the procedure, its benefits, and any potential risks or side effects. It is important for patients to understand that electrical stimulation is a non-invasive treatment method that uses low-level electrical currents to stimulate nerves and muscles.
During the initial consultation, healthcare providers will educate patients on how electrical stimulation works and what they can expect during the treatment process. They will explain that different types of electrical stimulation may be used depending on their specific condition, such as transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) or neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES). Patients will also be informed about the importance of adhering to scheduled treatments and following any recommended guidelines for optimal results.
In addition to providing information about the treatment itself, patient education includes teaching patients self-management techniques. This may involve instructing them on proper electrode placement, adjusting intensity levels within prescribed limits, and recognizing signs of discomfort or adverse reactions. By empowering patients with knowledge and skills related to their therapy, they become active participants in their own care journey.
Electrical stimulation is a therapeutic technique that uses electrical currents to stimulate nerves and muscles in the body.
Before starting electrical stimulation treatment, a thorough evaluation of the patient's condition is done, which may include medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
Electrical stimulation is commonly used for pain management, muscle strengthening, rehabilitation after injuries or surgeries, and to improve circulation and tissue healing.
The types of electrical stimulation include transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES), interferential current (IFC) therapy, and functional electrical stimulation (FES).
The treatment process involves placing electrodes on the skin near the targeted area, which deliver electrical currents to stimulate nerves and muscles. The intensity and frequency of the stimulation will be adjusted based on the individual's needs.
Electrical stimulation can help reduce pain, improve muscle strength and function, increase range of motion, promote tissue healing, and enhance overall rehabilitation outcomes.
While electrical stimulation is generally safe, there are some precautions and contraindications to consider. These may include avoiding use over areas of infection, open wounds, or broken skin, and avoiding use for individuals with pacemakers or certain medical conditions. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting electrical stimulation.
Yes, electrical stimulation can be combined with other therapies such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and massage therapy to enhance the overall treatment effectiveness and outcomes.
The expected outcomes may vary depending on the individual and their specific condition, but commonly include reduced pain, improved muscle strength and function, increased mobility, and enhanced overall rehabilitation progress.
Yes, patient education is crucial for understanding the treatment process, managing expectations, and ensuring the safe and effective use of electrical stimulation.
Copyright © Car Accident Doctors Group. All Rights Reserved